Variable application of fertilizers (especially nitrogen) is usually the first variable application implemented by farms. The benefits of these applications are instantaneous and allow the most efficient use of nitrogen to increase yield even under increasingly stringent conditions of the nitrate directive. Variable application of fertilizers is based on the need to approach different parts of the field differently, depending on the yield potential in its individual parts.
The basic element for variable application of fertilizers is the processing of a map of relative yield potential. This map divides the fields into individual zones according to whether their yield potential is greater or lesser than other zones. The zones are given as a percentage (e.g. 95%, 100%, 105% etc.) and express how much the zone is better or worse than the average. Careful processing of relative yield potential maps is the basis for the properly performed variable application. Thanks to the variable application, the correct fertilizer dose is applied and the environment is not wasted and burdened, as is the case with homogeneous fertilization.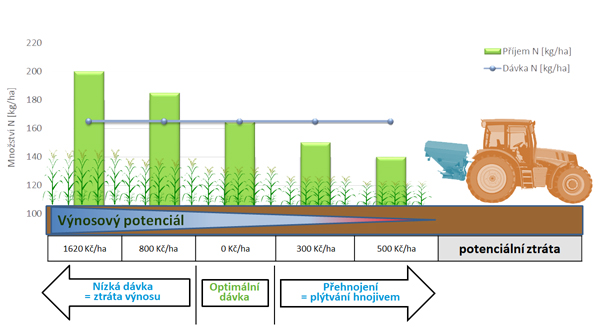
Since the master of the field is always an agronomist, it is he who decides what fertilizer and in what dose it will be applied to the field. After filling in a simple table, the application map is uploaded remotely to the machine terminal and the application can start.